In the academic realm, scholars have it drilled into their heads that academic dishonesty like duplicating other authors’ content and ideas is entirely unacceptable. Whereby engaging in any of the various types of plagiarism can come with severe consequences, not only resulting in you failing your assignments but also potentially costing you your academic career.
Exploring the different types of Plagiarism
In the academic environment, plagiarism is the act of copying someone else’s work and presenting it as your own. While that is the essence of this concept, there is much more to it than what the definition suggests. Plagiarizing other people’s work can be done in different ways, and it can be either accidental or deliberate. How so? When you are writing your research you might copy a few sentences or the whole text, copy work by tweaking a few phrases here and there, or even copy yourself, but all this will still land you in trouble. But do not worry we’ve got you covered to help you understand the different forms of plagiarism to prevent yourself from making fatal mistakes and copying content.
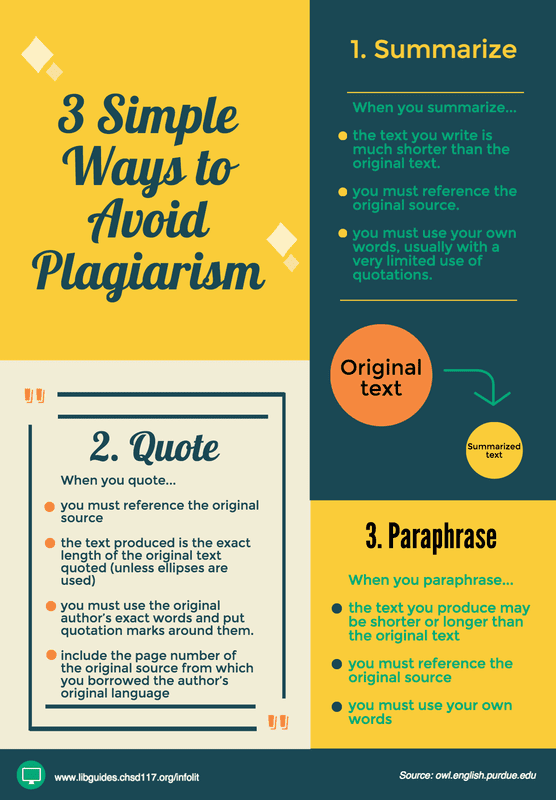
How can we stop plagiarizing and stealing other authors’ intellectual property? The first step to avoiding plagiarism is knowing what it is, and the various ways in which it shows up in writing, particularly in academic settings. Once you know the common types of plagiarism, it’s easier to avoid them in your writing.
Direct plagiarism
When many students think of plagiarism, direct plagiarism comes to mind first. Also known as verbatim plagiarism, this is one of the most serious forms of academic offenses. What does it entail? It involves deliberately copying your sources word for word without citing them trying to claim ownership of the work falsely and making most of your content plain copy and paste of someone else’s ideas. It may include:
- Reusing the entire paper written by another person and presenting it as your work.
- Using large sections of text from a source and failing to cite nor give proper acknowledgment.
- Using a relatively small section of text from another person’s work and failing to provide citations and quotation marks to show that the text is from another.
- Using data, charts visual representations, or graphs prepared by others without acknowledging the source.
Students and authors try to avoid being caught by simply deleting a few sentences or paraphrasing them slightly. However, even with the minor changes to the structure, if your paper consists of mainly copied work that has not been properly cited, it is a type of direct plagiarism. This form of plagiarism incorporates cheating and intentional plagiarism, where the writer lacks skills and understanding of academic norms thus leading to unintended consequences. Direct plagiarism in an academic paper will always result in an automatic zero. Furthermore, in the professional world, it can end in losing a job or a client. Academic integrity is not taken lightly in both situations and disciplinary action can be necessary.
Self-plagiarism
Self-plagiarism is often defined as reusing or recycling one’s own specific words from previously published text. How is this plagiarism? Well, you may wonder, while it does not cross the line of true theft of others’ ideas, it nonetheless can create issues in the scholarly publishing world. Beyond the direct plagiarism section of the text, self-plagiarism can also refer to the publication of identical papers in two places. Additionally, the best practice is to cite your previous work thoroughly, so that when you are simply revisiting an old idea. In simple terms,
self-plagiarism is any attempt at any of your previously published text, or research papers, and make it appear brand new.
Paraphrasing plagiarism
Paraphrasing plagiarism is quite difficult to spot in academic and professional writing. Why? In this type of plagiarism, instead of stealing a direct quote, the writer steals an idea by paraphrasing a quote without citation. Reusing an author’s original thought without citing is just as bad as copying their exact wording and therefore punishable in academic and professional settings.
Paraphrasing plagiarism is like mosaic plagiarism; however, it is usually more of a general summation of an idea than a sentence rephrasing. It is considered common knowledge such as universal laws of physics.
Mosaic plagiarism
This is another form of plagiarism that raises a lot of concerns. Why? Well, for mosaic plagiarism, also known as patchwriting scholars have not copied the original author’s work word for word but they may have borrowed paragraphs and later paraphrased, however, the structure of the work is maintained. Luckily most plagiarism checkers might not be able to detect this type of copying, but it is still unethical, dishonest, and illegal. Mosaic plagiarism includes:
- When a writer merely deletes some words from an included text but does not indicate the portions that are directly quoted.
- It occurs when a writer substitutes synonyms for some word or phrase in an included text without indicating the directly quoted material.
- Situations where a writer varies the grammatical structures slightly from the original text but retains the character and language of the original text.
Generally, writing research considers that many instances of patchwriting are examples of unintentional plagiarism that reflects the writer’s difficulty in fully understanding the source material or the standard appropriate source use. Patchwriting, while still constituting plagiarism, might not indicate academic dishonesty. Patchwriting can be used as a tool to improve students’ understanding of difficult academic material.
Accidental plagiarism
There is no excuse for plagiarism, whether intended or unintended the consequences are the same. However, plagiarism can be accidental if it occurs due to neglect, mistake, or unintentional paraphrasing. In most institutions, scholars are most likely to fall victim to accidental plagiarism. Therefore, universities should stress the importance of education about this form of plagiarism. Students are usually encouraged to learn how to cite their sources and to take careful and accurate notes when doing research. Additionally, lack of intent does not absolve the student of responsibility for plagiarism. Cases of accidental plagiarism are taken as seriously as any other plagiarism and the consequences are the same as the other types of plagiarism.
Inaccurate authorship
When you are citing different sources, you must do it correctly. Everyone involved in researching, editing, or writing the source, especially in scientific studies with multiple authors and editors needs to be appropriately credited. If this is not adhered to then it is considered incorrect authorship and a form of plagiarism.
What is considered incarnate authorship and how does it occur? Inaccurate authorship occurs when a citation does not include an original author or edit of the source. It can also happen when you give credit to an author or editor who did not work on the source. Either way, this violates the codes of research integrity and is thus unaccepted in an academic paper.
Preventing plagiarism: How to avoid plagiarism

How to avoid direct plagiarism
It is one of the most common and easiest forms of plagiarism to avoid. For starters, write your papers, this is not the time or place to earn on your classmates. Try as much as possible to use quotation marks around direct quotes and cite every source at the end of the essay and within the text. The type of in-text citations will vary depending on the writing style, but they are always necessary.
How to avoid self-plagiarism
Is it possible to avoid self-plagiarism? Yes. One of the easiest ways to avoid accidentally plagiarizing yourself is simply not to rewrite papers from high school for college essays or even worse, papers from other college classes. For instance, if you are required to write on the same subject in two different situations, start from scratch instead of trying to copy parts of the original paper. While you can use the same sources from the original works, it is important to avoid plagiarism.
How to avoid paraphrasing plagiarism
To avoid falling victim to paraphrasing plagiarism, avoid writing content directly after looking at the source. It is easy to accidentally plagiarize when you do not carry out proper research, instead, you find yourself simply duplicating something that you have learned online. Plan out your essay, have an outline, and take note of all your sources.
Conclusion
But is there a way to avoid inaccurate plagiarism? The easiest way to avoid this mistake is to always double-check your citations. Ensure that you are providing proper attrition that aligns with your formatting guidelines for your work and that every author is correctly cited.
All these types of plagiarism mentioned above have their consequences. Plagiarism in all forms is condemned and you may be penalized for this. If you engage in plagiarism early in your schooling process, you will initially be punished with a low grade in a specific subject, but not only that. You risk being suspended or even expelled from college/school altogether. As a result of plagiarism, your academic career will be penalized, being expelled from the college for plagiarism, it will be difficult or almost impossible to continue your education in another college and as a result, you will not be able to build a decent career academic.


